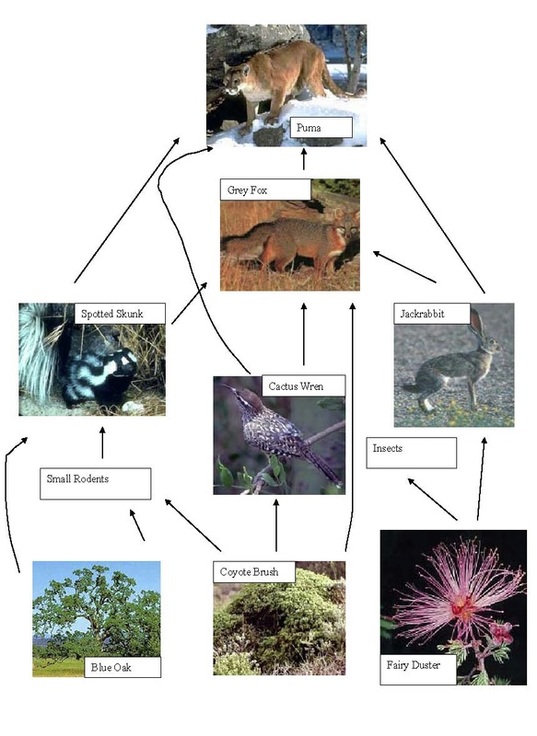
Food Web of the Chaparral
Producers: Common producers in the California Chaparral include the Blue Oak, the Coyote Brush and the Fairy Duster. Plants in the Chaparral must be adapted to irregular rainfall, drought and fire. For example, the Blue Oak, which is native to California, has an extensive root system and a waxy coating on its leaves. The Coyote Brush has a flame retardant chemical makeup and flame retardant leaves. Neither plant is endangered due to their ability to adapt.
Primary Consumers: Primary consumers in the California include small rodents, insects, hares (like the Jackrabbit) and birds (Cactus Wren). Furthermore, many animals like the Spotted Skunk and the Grey Fox are omnivores, eating both plants and animals. Currently the California Chaparral is disappearing due to urbanization and development. As this occurs, the Cactus Wren is continually losing its habitat. However, the Cactus Wren is not yet threatened or endangered due to its adaptability though it is protected by the Migratory Bird Treaty Act. The Jackrabbit, the Spotted Skunk and the Grey Fox are plentiful in the wild.
Secondary/Tertiary Consumers: Secondary and tertiary consumers in the California Chaparral include the Grey Fox and the Puma as well as other large mountain lions and cats. Currently the Puma is fully protected from hunting in California. Other threatened/endangered consumers not pictured include the San Joachim Kit Fox and the Island Grey Fox.
Scavengers and Decomposers: Coyotes (opportunists) are prevalent in the California Chaparral. Other decomposers include basic fungi and bacteria.
Primary Consumers: Primary consumers in the California include small rodents, insects, hares (like the Jackrabbit) and birds (Cactus Wren). Furthermore, many animals like the Spotted Skunk and the Grey Fox are omnivores, eating both plants and animals. Currently the California Chaparral is disappearing due to urbanization and development. As this occurs, the Cactus Wren is continually losing its habitat. However, the Cactus Wren is not yet threatened or endangered due to its adaptability though it is protected by the Migratory Bird Treaty Act. The Jackrabbit, the Spotted Skunk and the Grey Fox are plentiful in the wild.
Secondary/Tertiary Consumers: Secondary and tertiary consumers in the California Chaparral include the Grey Fox and the Puma as well as other large mountain lions and cats. Currently the Puma is fully protected from hunting in California. Other threatened/endangered consumers not pictured include the San Joachim Kit Fox and the Island Grey Fox.
Scavengers and Decomposers: Coyotes (opportunists) are prevalent in the California Chaparral. Other decomposers include basic fungi and bacteria.